What is cancer?
Cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal body cells. Cancer develops when the normal body control mechanism stops functioning. Old cells do not die and grow out of control but rather produce new, dysfunctional cells. These extra cells may form a mass of the tissue, called a tumor. A tumor may also be cancer.
Skin Cancer
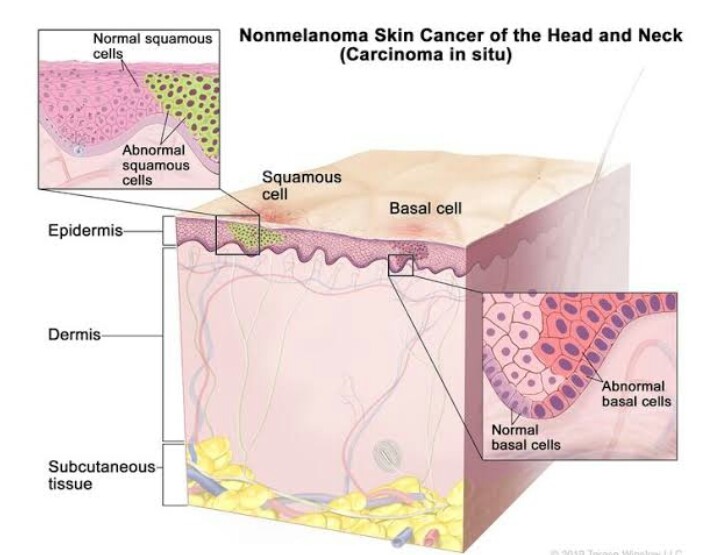
Skin cancer is the out-of-control growth of irregular cells in the outermost layer of the epidermis caused by the mutation-causing unrepaired DNA damage. These mutations lead to the rapid proliferation of skin cells and malignant tumor growth.
Skin cancer is most common among people working outside, sunbathing, or playing sports. About 3.3 million people in the US are diagnosed with more than 5.4 million new cases of cancer each year.
Skin cancer- Types
The skin covering our body is the largest organ of the integumentary system. It protects us against the wind, sunlight, injury, and infections. Skin also helps control the body temperature and stores vitamin D, fat, and oxygen. The skin has many layers, but the two primary layers are the epidermis (upper or outer layer), and the dermis (lower or inner layer). Skin cancer starts in the epidermis, and consists of three cell types:
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinomas (BCCs) are abnormal, uncontrolled growths that arise in the outermost skin layer (epidermis) from the base cells of the skin. These cancers most frequently occur in areas of the skin that are normally exposed to the sun, especially the face, ears, neck, scalp, shoulders, and back. BCCs can be locally destructive if not detected early and treated. It is usually not life-threatening.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is an unregulated growth of anomalous cells from the squamous cells in the outermost layer of skin (epidermis). Many SCCs cause long-term chronic exposure from the sunbeds to UV rays and tanning beds. SCC is the second most prevalent type of skin cancer. Every year more than 1 million cases are diagnosed in the United States. SCCs can often develop quickly, and metastasize unless detected and treated early.
Melanocytes
Melanoma is cancer that grows from melanocytes, the skin cells that contain melanin pigment that gives skin color. Melanomas also mimic moles, and may often emerge from them. These may be present on any part of the body, even in areas that are not normally exposed to the light. Melanoma is often caused by the kind of severe, sporadic sun exposure that results in sunburn. It broadly spreads to other major organs, such as the liver, lungs, brain, and bones. There are expected to be more than 196,060 new cases of melanoma in the United States in 2020, of which about 100,350 would be harmful.
Causes of skin cancer
Following are the causes of skin cancer:
• Two deaths in three of active long term smokers can be attributed directly to smoking
• Almost 4.5 percent of cancers are linked to alcohol
• Most cancers result directly from dietary factors, from infectious agents or from exposure to radiation (especially UV skin cancers)
• Inherited ‘fault’ genes cause certain cancers
• Cancer is NOT from mistake or stress.
• A weakened immune system
• High-altitude or sunny climates
Skin cancer-Symptoms
Get familiar with the look of your skin and you’ll pick up any changes that might suggest a skin cancer. Search:
• Any crusty, non-healing sores
• Small red, pale or pearly lumps in color;
• New spots, freckles or other moles that change in color, thickness or shape for weeks to months
Skin cancer-Treatment
Most cases of skin cancer can be treated with outpatient surgery or in a dermatologist’s clinic. However, more serious skin cancers like melanoma or Merkel cell carcinoma can develop tumors and require more intensive care, such as surgery, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy.
The most common treatment for skin cancer consists of:
Surgery
Most skin cancers are surgically treated, notably basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas, which are usually removed by a dermatologist as part of an outpatient procedure.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be a choice in patients with advanced skin cancer, such as Merkel cell carcinoma which has spread elsewhere in the body. These anticancer drugs are designed to stop or delay the growth of tumor cells which divide rapidly.
Radiation therapy
Radiation treatments for killing remaining cancer cells in the area where lymph nodes have been removed may be recommended after surgery. This procedure can also be used to treat chronic skin cancer to relieve symptoms or limit the spread of disease (metastasis).
Hair Loss(Causes, Symptoms, Treatment)





0 Comments