What is Heart Failure? It is an ongoing, reformist condition in which the heart muscle can’t siphon enough blood to address the body’s issues for blood and oxygen.
What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure is a constant infection of the heart wherein the heart can not siphon enough blood as per the prerequisites of body tissues. At the point when the flexibility and request of oxygen are not in equilibrium in view of low cardiovascular yield, the condition is known as a cardiovascular breakdown. The most well-known reasons for cardiovascular breakdown are coronary corridor infection, hypertension, arteriosclerosis, myocardial dead tissue, hypertension, cardiomyopathy, and inherent heart issue.
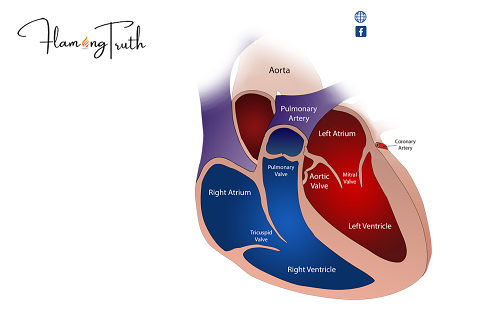
What is the physiology of a normal heart?
The heart itself comprises 4 chambers, 2 atria, and 2 ventricles. De-oxygenated blood re-visitations of the correct side of the heart by means of the venous course. It is siphoned into the correct ventricle and afterward to the lungs where carbon dioxide is delivered and oxygen is retained.
The human heart is an organ that siphons blood throughout the body by the circulatory framework, providing oxygen and supplements to the tissues and eliminating carbon dioxide and different squander. The tissues of the body need a consistent gracefulness of nourishment to be dynamic.
Blood conveys oxygen and other significant supplements that all body organs require remaining solid and to work appropriately. Your heart is a muscle, and its responsibility is to siphon blood throughout your circulatory framework.
The right ventricle siphons the oxygen-helpless blood to the lungs through the pulmonary valve. The left chamber gets oxygen-rich blood from the lungs and siphons it to one side, ventricle through the mitral valve. The left ventricle siphons the oxygen-rich blood through the aortic valve out to the rest of the body.
What is the Heart Failure?
There are two types of heart failure :
- Systolic heart failure
- Diastolic heart failure
-
Systolic Heart Failure:
Systolic cardiovascular breakdown happens when the left ventricle of your heart can’t contract totally. That implies your heart won’t siphon strongly enough to move your blood throughout your body effectively. It’s likewise called cardiovascular breakdown with decreased launch part.
-
Diastolic Heart Failure:
- Diastolic cardiovascular breakdown, a significant reason for bleakness and mortality, is characterized as an indication of a cardiovascular breakdown in a patient with safeguarded left ventricular capacity. It is portrayed by a firm left ventricle with diminished consistence and impeded unwinding, which prompts expanded end-diastolic weight.
What are the Stages of Heart Failure?
There are four phases of heart failure named 1, 2, 3, 4. Understanding once moved to arrange B can’t move back to organize A. Subsequently heart failure is a reformist sickness.
-
Stage 1:
- This is the territory of Pre-cardiovascular breakdown, which implies that the patient is in danger to create a cardiovascular breakdown. There are no basic coronary illness or indications of cardiovascular breakdown.
- Patients may have a family background of coronary illness and some comorbidities that may prompt cardiovascular breakdown. Danger elements of a cardiovascular breakdown in stage An area of Hypertension, diabetes, stoutness, metabolic illness, exorbitant utilization of liquor, family background of heart sickness, coronary vein infection, or utilization of meds that may cause a cardiovascular breakdown.
-
Stage 2:
It is likewise a pre-cardiovascular breakdown stage, yet with auxiliary coronary illness. On the off chance that a patient has been determined to have left ventricular brokenness yet not having any indications of a cardiovascular breakdown, it is viewed as that patient is remaining at Stage 2.
In this stage, the patient is having a launch division of under 40%, as per the Echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart).
-
Stage 3:
Patients that are having Stage 2 cardiovascular breakdown have recently been determined to have HF and may have or had signs and side effects of cardiovascular breakdown. This is a further developed stage with the accompanying manifestations:
- Weakness (due to lacking oxygen gracefully to tissues)
- Breathlessness
- Lethargy
- Edema
-
Stage 4:
Stage 4 of cardiovascular breakdown is related to the side effects that can’t be treated with prescription or steady treatment. The patient is expected to hospitalize repetitively despite all treatment measures. This is the end-phase of cardiovascular breakdown.
Frequently Asked Question:
1. How long can you live with heart failure?
The normal life expectancy for patients with coronary illness is variable, as shown by infection. Some different variables, like the age of the patient, hereditary profile, and different comorbidities additionally decide how long a heart patient can live. According to the exploration of the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), half of the patients with a cardiovascular breakdown can live over five years on the off chance that they are disciple to medicine and preventive measures.
2. What is the primary cause of cardiovascular breakdown?
A few different infections, including diabetes, arteriosclerosis, myocardial dead tissue, weight, hypertension, and coronary corridor imperfections can be a significant reason for cardiovascular breakdown. Family background of cardiomyopathy and innate coronary illness can likewise be a purpose behind the cardiovascular breakdown.
3. Can depression cause a heart attack?
In the people that are now experiencing cardiovascular sickness, sorrow 1 can fuel the condition. While in the individuals with no past heart issue, melancholy tension and stress can upgrade the odds of creating coronary illness and respiratory failure.
4. Is low blood pressure a symptom of heart failure?
Decently low or incredibly low circulatory strain shows that the myocardial muscles have become so debilitated that the heart can’t contract appropriately and siphoning of blood is troublesome, bringing about low cardiovascular yield. Low pulse and syncope indicate coronary illness and perhaps cardiovascular breakdown.
Conclusion
Heart failure is a persistent, reformist problem of the heart that happens because of some basic reason, for instance, myocardial localized necrosis, cardiomyopathy, hypertension, or ischemic coronary illness, and so on Ordinary physiological boundaries including preload, afterload, contractility, and cardiovascular yield if getting upset, can cause a cardiovascular breakdown. Beta-blockers, vasodilators, ACEIs, Barbs, Aldosterone opponents, inotropic specialists, and diuretics are the favored treatment for a cardiovascular breakdown.













0 Comments